Periodontics and Treatments
Periodontal dentistry or Periodontics is a dental specialty that deals in the treatment of the gum tissue supporting the teeth.
Periodontal Exam
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for your dental and overall health. A periodontal examination can identify many problems before they advance into complex and permanent problems.
Periodontal disease is gum disease, an infection of the gum tissue and bone surrounding the teeth. An estimated 80% of the adult population has periodontal disease at one stage or another.
Periodontal bacteria causes inflammation and destruction of the gum tissue that connect teeth to bone. As gum tissue is lost, a space called a periodontal pocket is created. A small amount of pocketing with 1 to 3 mm depths is normal. Proper daily brushing and flossing helps to keep these pockets clean. When pockets are greater than 3 mm in depth, it is impossible for you to clean and maintain them without periodontal treatment. As a result, bacteria multiply in deeper pockets and cause chronic gum infection.
As people age, we become more vulnerable to periodontal bacteria. Without periodontal treatment, teeth lose gum support, become loose and painful, and are eventually lost.
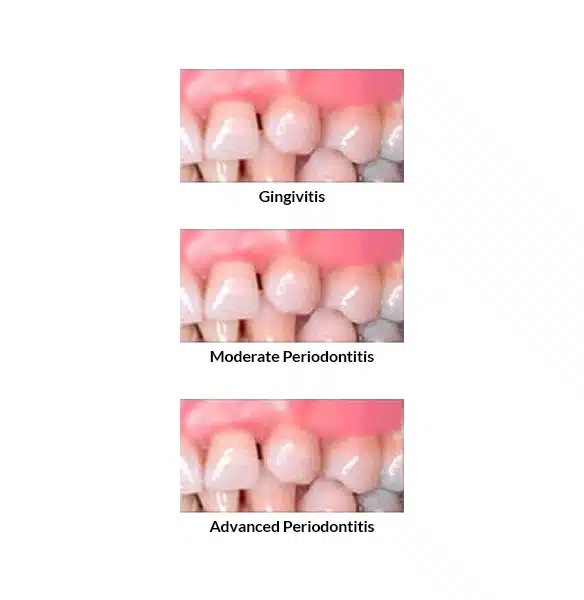
Stages of Periodontal Disease
- Gingivitis - Early stage gum disease where the gums become swollen, tender, and are likely to bleed. With proper oral hygiene and treatment from your dentist, gingivitis is reversible.
- Moderate Periodontitis - Moderate stage gum disease where the gums have deteriorated and begin to detach from the teeth. Periodontal gum pockets are deep enough to allows plaque to collect below the gum line. Bacterial in the pockets multiply rapidly. Tooth roots become susceptible to decay, and periodontal disease requires immediate treatment.
- Advanced Periodontitis - Advanced gum tissue and bone loss occur. Teeth become loose and may require extraction. Chewing and biting become painful and difficult. Untreated, patients risk the loss of teeth and serious health complications.

Some factors increase the risk of developing periodontal disease:
Bridges that do not fit properly
Crooked teeth
Fillings that have become defective
Pregnancy or use of oral contraceptives
Medications such as steroids, some anti-epilepsy drugs, anti-cancer therapy drugs, some oral contraceptives and calcium channel blockers
Systemic diseases such as diabetes
Tobacco smoking or chewing
Warning signs of periodontal problems:
A change in the fit of partial dentures
A change in you bite, and the way your teeth fit together
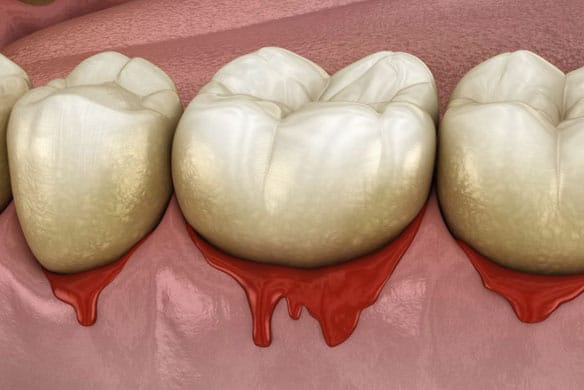
Gums that bleed easily
Gums that have receded away from the teeth
Permanent teeth that are loose or separating
Persistent bad breath or bad taste
Red, swollen, tender gums
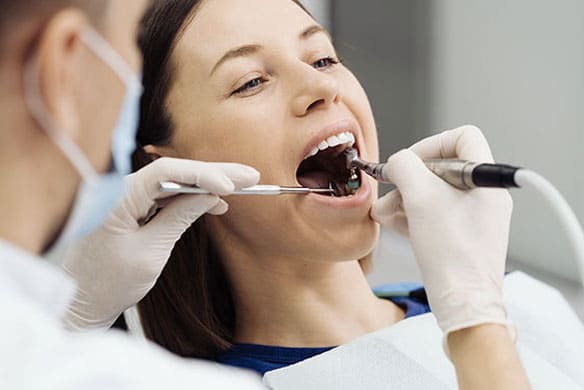
Common periodontal procedures:
Scaling and root planing - Immediate and non-surgical periodontal procedures where a dental hygienist removes tartar and plaque from the teeth below the gums.
Tissue Graft - Periodontal tissue augmentation can cover sensitive or exposed roots with relocated gum tissue. Tissue grafting procedures improve aesthetics, provide a band of gum tissue around the base of treated teeth and improves long-term prognosis for saving teeth.
Medication - Antibiotics or irrigation with anti-microbial mouth rinses help to reduce the growth of periodontal bacteria cause periodontitis.
